What is a Market and the Marketing Department?
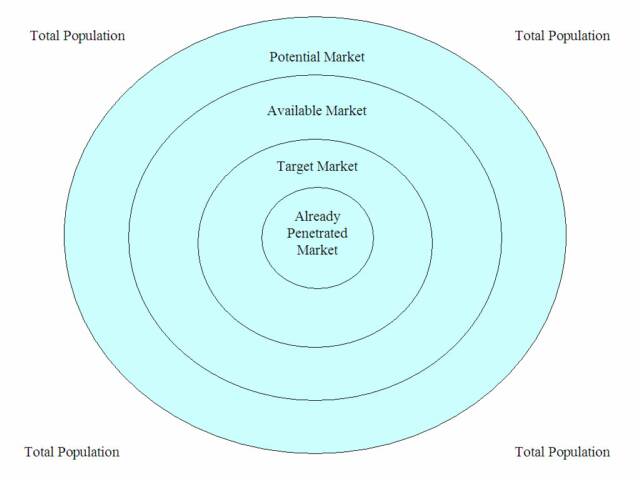
A Market is a group of customers or potential customers. Companies focus on its particular market by getting practical information the company can use for sales, marketing, and product development. The market starts with the total population, then Potential markets that have an interest, then Available markets that have the money, then Target markets that are the customers the company has determined to serve (the served market), then finally the Penetrated markets who have already bought your products and/or services.
The market can then be broken up into segments and analyzed even further. We will review market segments later in this lesson.
The Marketing Department’s key responsibilities is to determine the needs, wants, and demands of the consumer and finds ways to satisfy those needs within its product base. Needs represents items such as food, housing, and clothing, whereas wants represents cultural based items such as makeup or vacations. Demands are simply the wants of a consumer who has the ability to pay for what they want.
Marketing deals with goods (which are tangible), services (an intangible benefit to customer’s), and ideas (concepts, images, etc). Quite often, as in this lesson, the word product can also refer to goods, services, or ideas.
Once the market has been establish, the marketing department looks at ways to best market the company’s product. Marketing does more than just promotion, they dig deep to find, or even try to create, consumer trends related to what their company is all about. Marketing needs to know and understand the customer to the point where selling is almost non-essential, and the product or service can sell itself.
Marketers need to be creative people as there is a lot of competition out there. Due to this continuous competition, the cycle of creating something new never ends. A key objective of marketing is to provide products and services that customers really want. They need to make customers feel they have a good relationship with the company. In this way the customer feels more like a partner, not just a source of revenue for the company. Marketing is always trying to develop satisfying relationships with customers that benefit both the customer and the organization.
Marketing needs to know how their decisions could lead to problems for other departments within the company. For example, making a decision to incorporate advertising statements that are too generic can increase the amount of calls to customer support.
Just as there is a split in economics (microeconomics and macroeconomics), the same holds true for marketing. The marketing environment has similar components:
- Microenvironment deals with internal factors that can influence the company directly. The marketing department is always looking at new strategies and market approaches. They need to then get the rest of the company to follow their lead. The problem is most other departments are more resistance to change. Finance will be concerned about the cost, customer service will be concerned with the change in direction and the training needed, and R&D might have to look at a new development approach. The process of internal marketing is focused toward overcoming this resistance to change. The internal decision makers within the company need to look at the manpower, money, machinery, materials, and markets that are all part of the internal environment. Distribution channels such as suppliers, vendors, warehousing, and transportation of the product, are also part of the internal environment and will be affected by marketing planning and decisions. The same goes for outside marketing service agencies.
- Macroenvironment deals with the external factors outside of your company’s direct control. Demographic and Social trends, Economic issues which impacts what people can afford to buy, Environmental factors such as the availability and cost of raw materials, the cost of energy and levels of pollution, Technological rate of change, and Political pressures such as legislation and effects from agencies like the FDA, FCC, or EPA that can stop certain marketing moves.
Marketers must also understand emerging technology and applications in order to truly understand what the customer expects technically. It will also help spot potential business opportunities as well as potential threats.
Some considerations of a company’s marketing program are consumption that seeks to get people to purchase more and more, customer satisfaction that’s more concerned with happy customers than pushing a product people may not like, choice that gives many products to choose from (however may be costly to the company), and lifestyle that focuses on improving a person’s quality of life.
Whether the company operates as a for-profit, or as a not-for-profit, customers may believe a company is dynamic and creative based on its advertising message. Marketing must also concentrate their efforts on the market associated with their products. In order to put marketing efforts into play, marketing needs to develop a marketing strategy, design a marketing plan, and then implement the marketing plan. These subjects will be taught throughout this lesson.